One compresses. The other preserves. JPEG vs PNG is a classic showdown of speed versus precision. And if you’re serious about photography, understanding the difference is more than just nerdy knowledge. It’s a smart way to make your images look their best wherever they go.
In this post, we’ll walk you through the pros and cons of each format and show you when to use what, whether you’re sharing online, designing prints, or building your brand.

Table of contents
What Is A JPEG File?

JPEG (short for Joint Photographic Experts Group) is one of the most common image file types in the world. It’s known for its compression, which means it reduces file size by discarding some image data. This process is called lossy compression.
JPEGs are perfect for photographs and images with rich colors and gradients. They’re widely supported and load quickly, which makes them a favorite for websites, social media, and email attachments.
You might also like: Image File Format Guide: What’s the best Image File Format?
What Is A PNG File?

PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics. Unlike JPEGs, PNGs use lossless compression, which means they retain all image details, even after compression. PNGs also support transparency, allowing parts of the image to be see-through.
They’re ideal for logos, graphics, text-heavy images, and anything with sharp edges or a transparent background.
What Is The Difference Between Jpeg and Png?
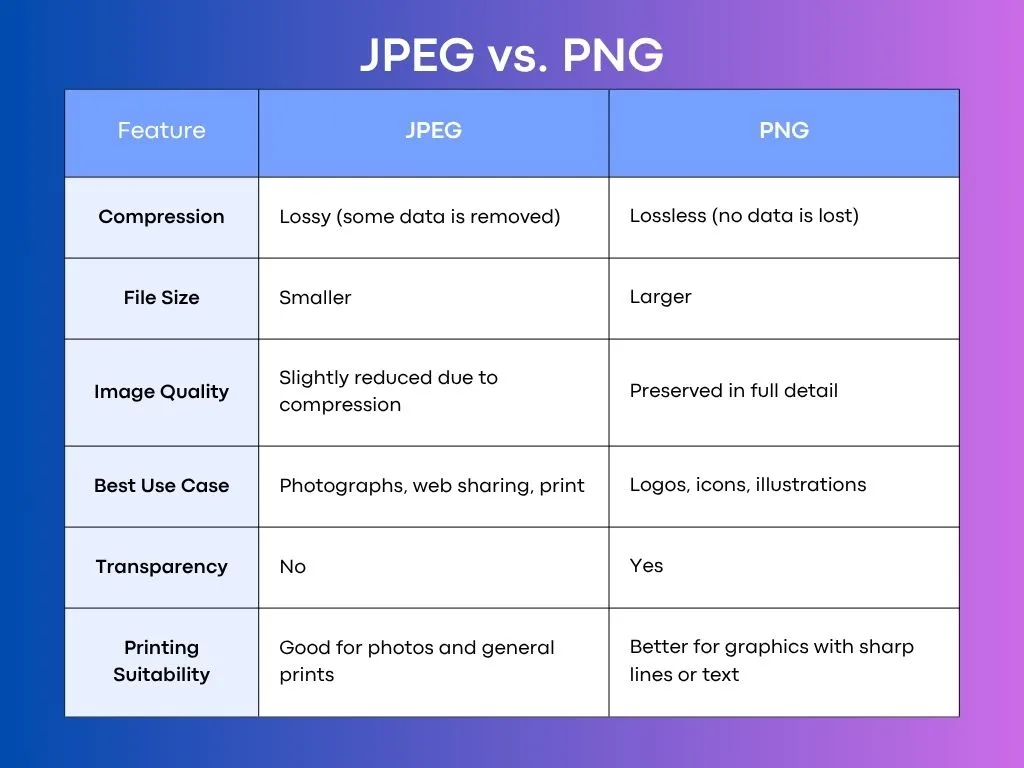
1. Compression
JPEG and PNG handle compression very differently. JPEG uses lossy compression, which means it reduces the file size by permanently removing some image data.
This helps reduce the file size, but it can also slightly compromise image quality, especially if you repeatedly save it.
PNG, on the other hand, uses lossless compression, which keeps all the image data intact. So, while PNG files are generally larger, they maintain perfect image quality no matter how many times you save them.
2. Image Quality
JPEG images can start to lose sharpness and exhibit compression artifacts (such as blurring or blocky areas) after repeated editing and saving. This is especially noticeable in images with text or clean lines.
PNG doesn’t have that issue. It keeps everything looking sharp and clear. That makes PNG the better choice when you need your image to look crisp and detailed, like in design elements or screenshots.
Also check out: Best tool to resize image in cm and kb.
3. Transparency Support
This is a big difference between the two formats. JPEG doesn’t support transparency at all. If your image has a background, it has to be a solid color.
PNG does support transparency, which means parts of the image can be fully or partially see-through. This makes PNG perfect for logos, stickers, and other graphics you want to place over other creative backgrounds without a visible box around them.
4. File Size
Because JPEG compresses more aggressively, its files are usually much smaller than PNGs. That’s why JPEG is often the go-to format for websites that need fast load times.
PNG files are larger because they retain more data and quality. This makes them ideal when image clarity is more important than storage space or speed.
5. Color Depth
Both JPEG and PNG support millions of colors, making them great for colorful images. However, PNG has the added advantage of supporting transparency through an alpha channel, giving it more control in design-heavy use cases.
For most everyday photography, JPEG is more than enough, but for professional design work or layering images, PNG can be more versatile.
You might also like: Free Photoshop Plugins For Effortless Editing
Key Benefits of JPEG

1. Smaller File Sizes for Faster Loading
JPEG is designed to compress images into significantly smaller file sizes without substantially affecting their appearance. This is especially helpful when you’re uploading photos to a website, sending them via email, or storing thousands of images on your device. The smaller size means quicker loading times and less strain on storage space.
2. Ideal For Complex Images
JPEG handles gradients and color-rich images, such as portraits, landscapes, and event shots, exceptionally well. It can smoothly blend tones and textures, which makes it a perfect match for photography. Even with compression, the human eye often can’t spot the minor quality loss in a well-saved JPEG.
3. Universally Compatible
One of JPEG’s biggest advantages is that it is compatible with almost all devices. Whether you’re uploading to social media, editing in basic or advanced software, or viewing on any device, JPEG is supported. You won’t run into any issues opening or sharing it.
4. Great For Web Use & Social Media
Due to its compact size and compatibility, JPEG is the preferred format for bloggers, marketers, and casual users alike. Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and most websites automatically compress or optimize images, so starting with a JPEG is a perfect fit for the system.
You might also like: How To Sell Stock Photos Online | Top Websites To Earn Money
Key Benefits of PNG

1. Lossless Compression for Perfect Quality
PNG keeps every pixel intact. Unlike JPEG, it doesn’t lose detail when you save or re-save the image. That means the final output is exactly how you intended it to be, especially important for designers who want their work to stay flawless, even after editing.
2. Supports Transparent Backgrounds
This is where PNG truly stands out. It allows parts of an image to be fully or partially transparent, making it ideal for logos, cutouts, stickers, watermarks, and overlay graphics. You can easily place a PNG image on top of another background without any ugly white boxes around it.
3. Best for Graphics, Text, and UI Elements
PNG is incredibly sharp when it comes to preserving straight lines and crisp edges, making it the best choice for digital assets like icons, buttons, web graphics, and anything that includes text. There’s no weird blurring or distortion like you might see with a JPEG.
4. Excellent Color Accuracy & Detail
PNG supports millions of colors and handles things like shadows, fine lines, and gradients very well. This makes it suitable for professional visuals where color accuracy is crucial, such as digital illustrations, infographics, and product mockups.
You might also like: Top Photography Trends That Are Worth Following
When to Use JPEG vs PNG
JPEG Works Great When…

- You’re working with photographs – It’s ideal for portraits, landscapes, and travel shots with lots of colors and detail.
- You need smaller file sizes – Great for faster website loading or saving storage on your phone or computer.
- You’re uploading to social media – Platforms like Facebook and Instagram compress images anyway, so JPEG fits right in.
- Transparency isn’t required – JPEG doesn’t support transparent backgrounds, so it’s best for full images.
- You’re printing photos in bulk – JPEGs can be printed just fine, especially in standard sizes.
PNG Works Great When…
- You need a transparent background – Essential for logos, watermarks, stickers, and overlays.
- You’re creating digital graphics or UI elements – Ideal for icons, buttons, and illustrations that need to look clean.
- You want the best quality possible – PNG uses lossless compression, so every detail stays intact.
- You’re editing and saving the file multiple times – PNGs won’t degrade in quality, no matter how many edits you make.
- You’re sharing screenshots or text-heavy visuals – PNG keeps text and sharp lines crisp and easy to read.
In a Nutshell: JPEG vs PNG
Choosing between JPEG vs PNG really comes down to what you’re using the image for.
If you need a smaller file size, are working with photographs, or just want something that’s easy to share and upload quickly, JPEG is your go-to format. It’s efficient, universally supported, and perfect for everyday use.
On the other hand, if you prioritize crystal-clear quality, require transparency, or are working with logos, graphics, or web design elements, PNG is the preferred format. It keeps your image looking sharp and clean, no matter how many times you edit or save it.
FAQs On JPEG vs PNG
Q.1 Can I convert a JPEG file to PNG or vice versa?
Ans. Yes! You can easily convert between JPEG and PNG using image editors like Photoshop, free tools like Canva, or online basic converters. Please note that converting JPEG to PNG won’t recover lost quality.
Q.2 Why are PNG files larger than JPEGs?
Ans. Because PNGs don’t compress image data as aggressively as JPEGs. They keep every pixel intact, which is great for quality, but not so great for file size.
Q.3 Does JPEG support transparency?
Ans. Nope! JPEG doesn’t support transparency. If you need a transparent background (like for a logo), PNG is the way to go.
Q.4 Are PNG files better for printing?
Ans. Not always. For high-quality photo prints, formats such as TIFF or high-resolution JPEGs are often preferable. PNG is great for digital use, but isn’t always the top choice for print.
Q.5 Is PNG better for text and line art?
Ans. Absolutely! PNG keeps lines and edges super sharp, making it ideal for text-heavy images, diagrams, or line drawings.
Q.6 Does converting PNG to JPG reduce quality?
Ans. Yes. Since JPEG uses lossy compression, converting a crisp PNG to JPEG will likely result in a reduction in image quality, especially in text or fine details.
Like this post? Check out more fantastic photography content here.






